
microRNA
A microRNA (miRNA) is a small (~22 nts) non-coding and single-stranded RNA-molecule.

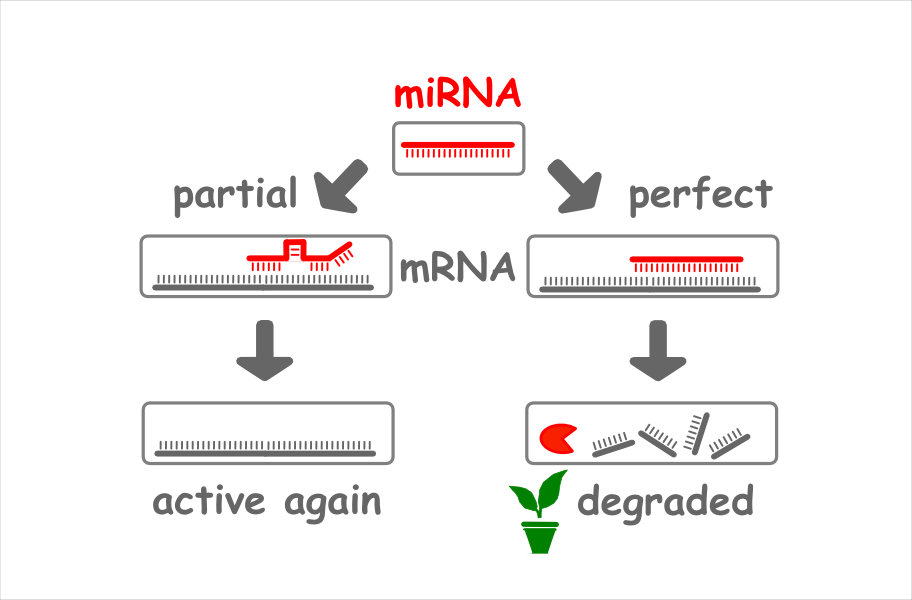
Gene Regulation by Complementary Binding
Its purpose is to regulate genes by binding complementarily to them.
If it binds partially, the translation of the target into a protein is repressed.
After the binding the target is active again.
If it binds perfectly, the target will be degraded. Usually you find this mechanism in plant organisms.

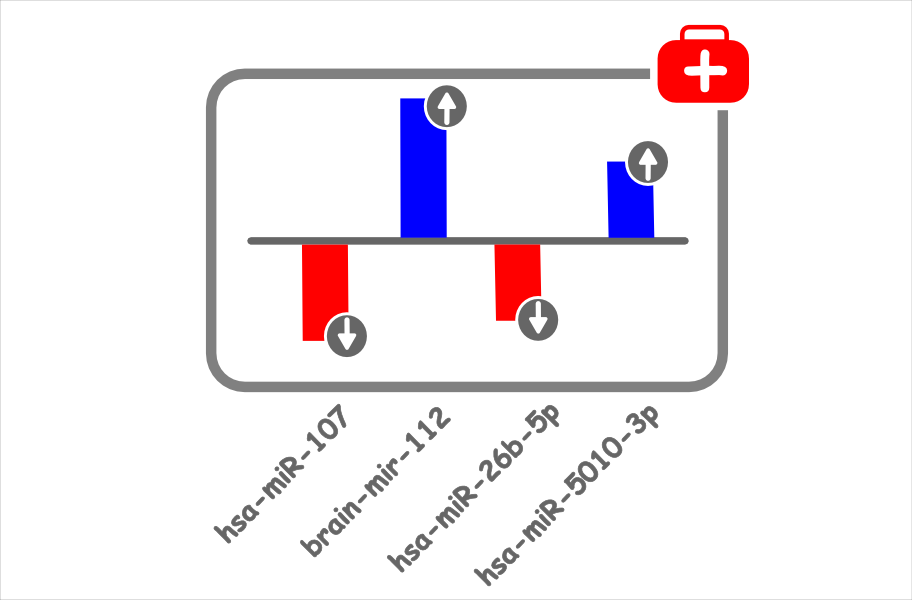
Medical Application: Biomarker
An deregulated miRNA can be used as a biomarker for distinguishing between health-states or different diseases.

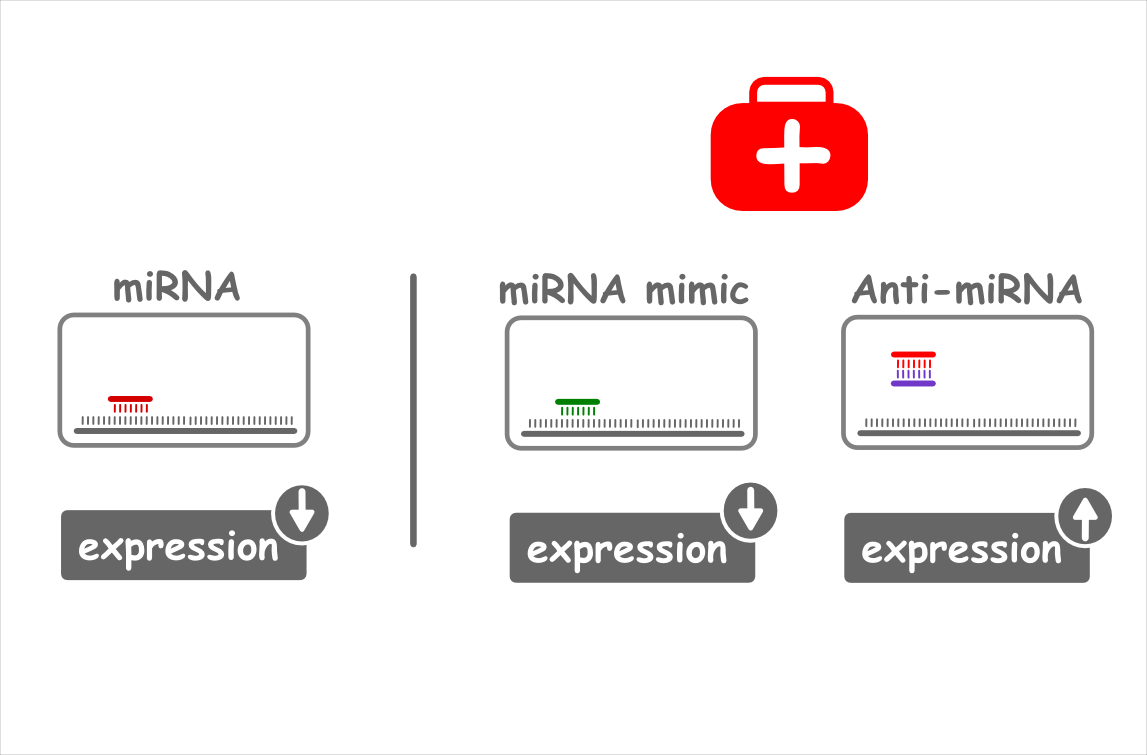
Medical Application: Gene Regulation
You can regulate the activity of a miRNA and its target with synthetic miRNA-like molecules.

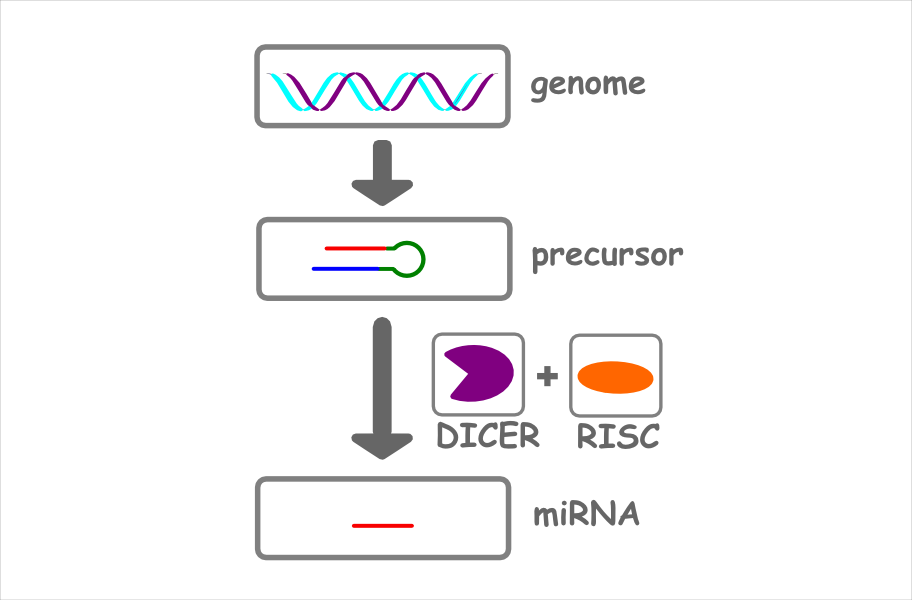
Biogenesis
Usually a miRNA is derived from a long precursor molecule.
The enzym DICER processes the precursor and the RISC complex selects if the 5p- or 3p-segment is the dominant active miRNA.

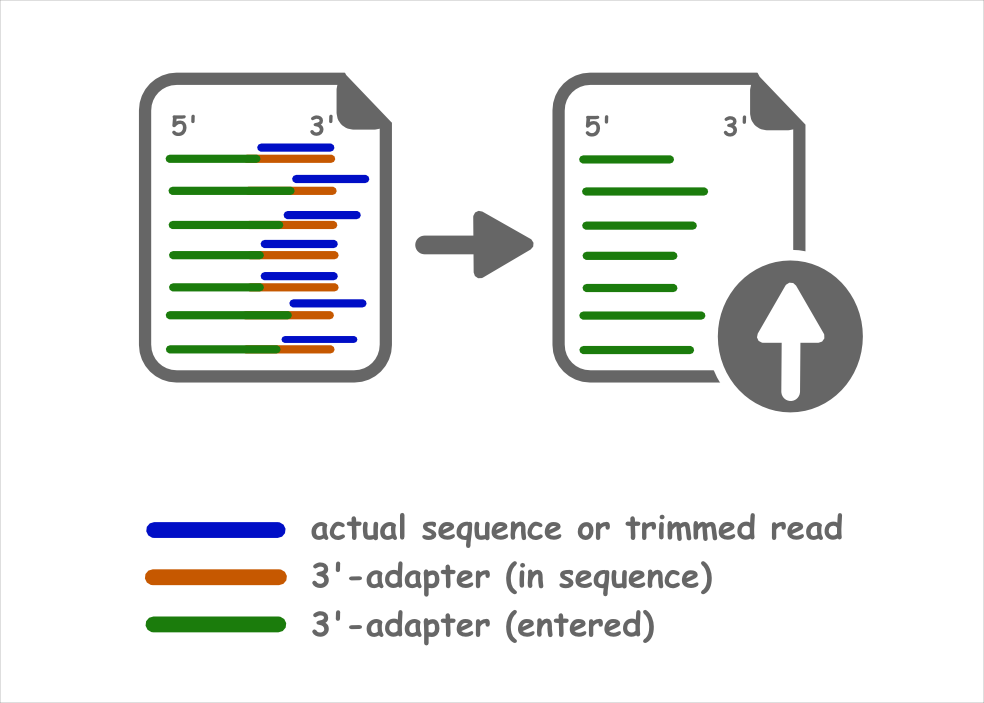
Preprocessing
On the user side, the input file will be preprocessed and simultaneously the trimmed sequences will be uploaded to our server.

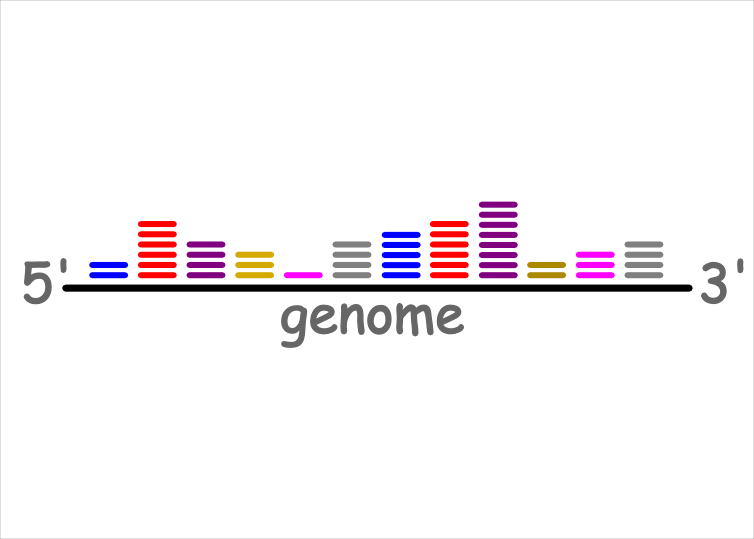
Mapping
On the server side, the sequences will be mapped against the species' genome.

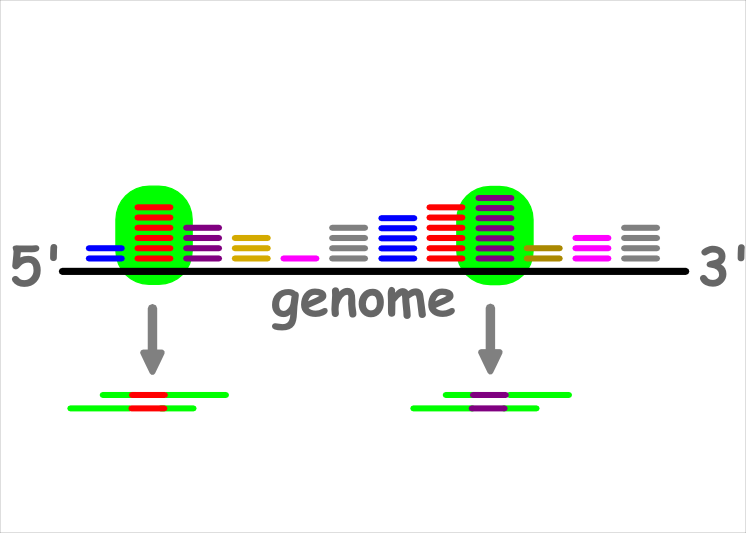
Precursor excision
Regarding high read mapping stacks (green circle), two potential precursors will be excised from these loci.

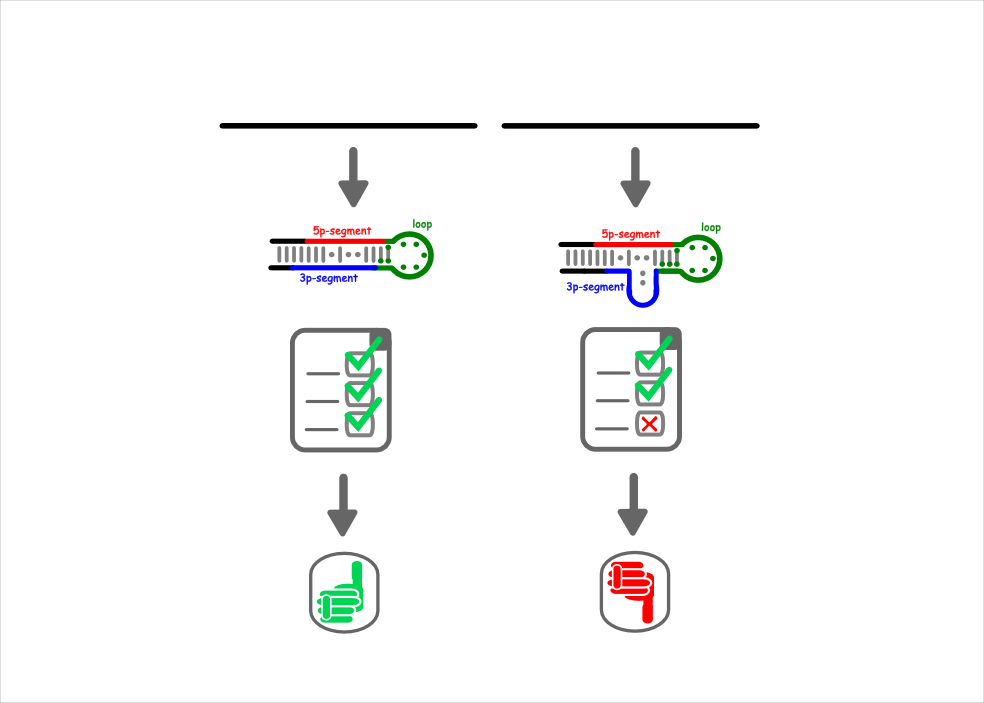
Structural Filtering
Potential precursors have to pass a structural test first.
In this test the structural features are checked.

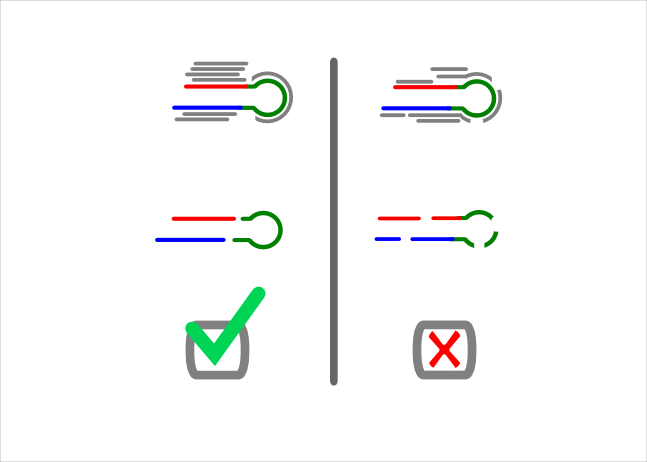
Signature Filtering
In the signature check, we test if the majority of the reads map consistently to the DICER processing.

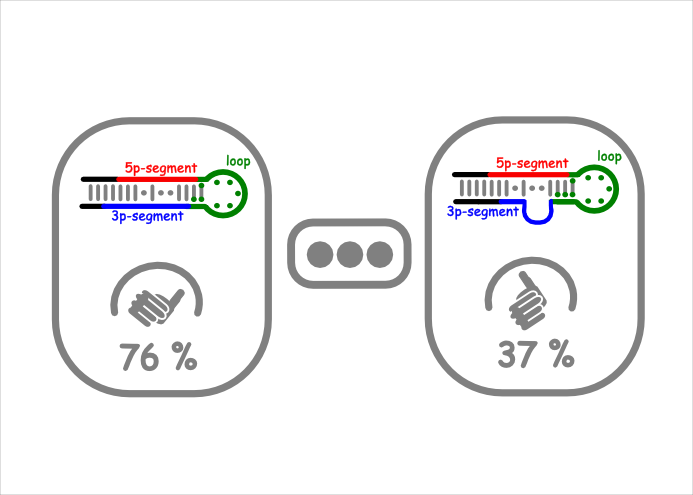
Prediction
We compute the probability of a potential precursor to be a real one.
<








Access to the Results
After selecting your first file, you can access the results by searching for your job or using the link that we will send you to your email adress.


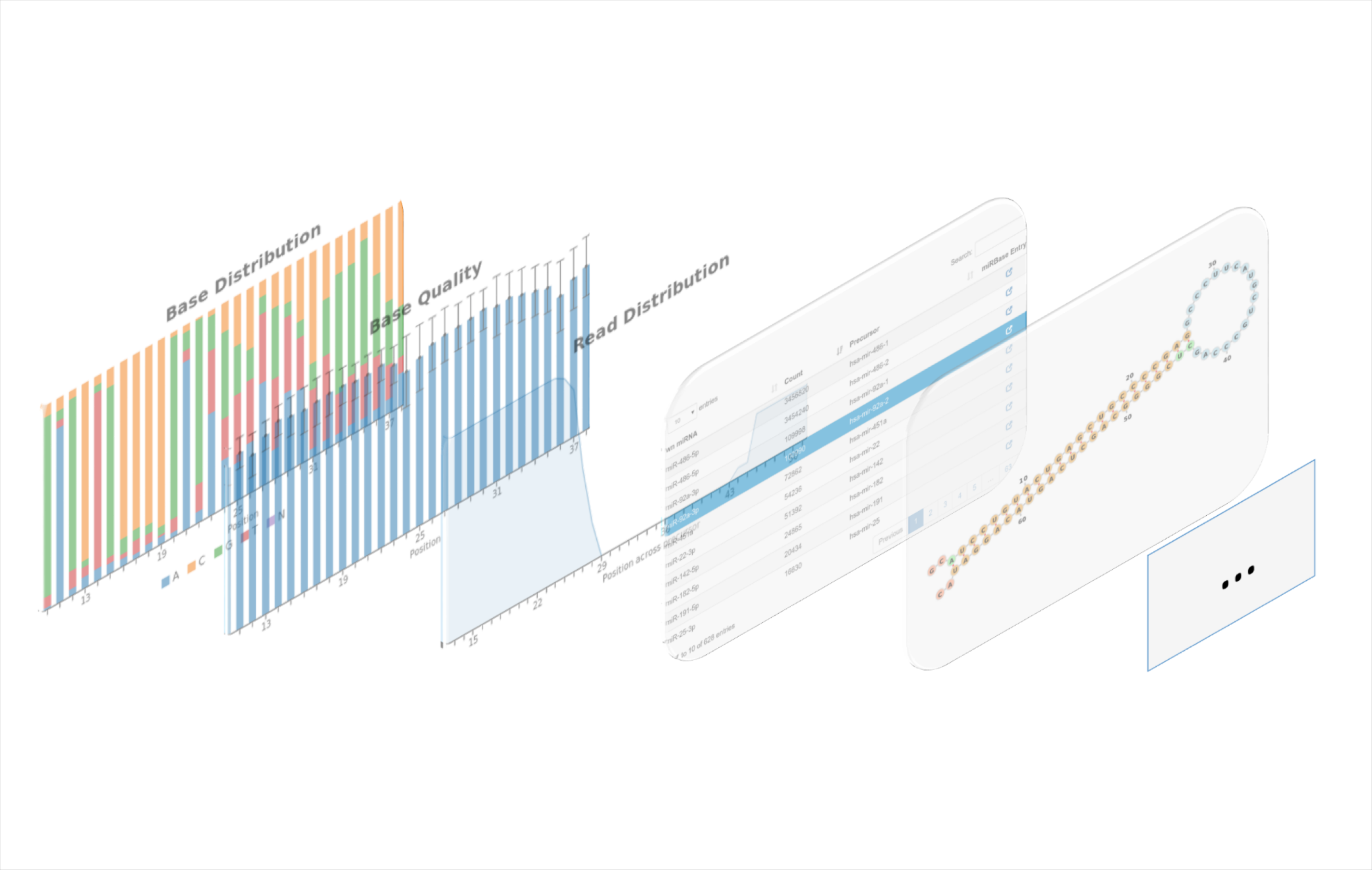
Variety of Results
We provide a variety of results for your experiment like total statistics for your files or details about a particular miRNA.


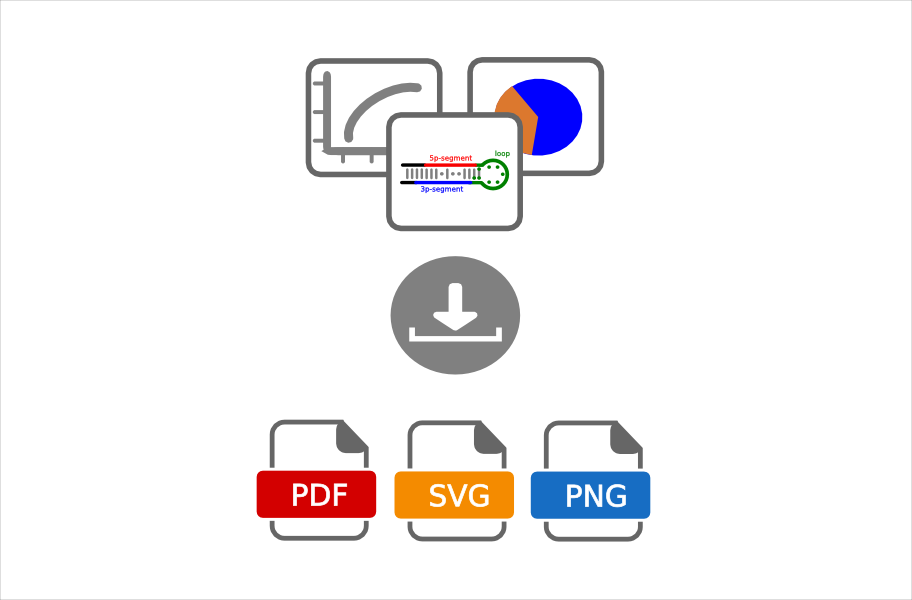
Export Your Results
You can download your online plots as pdf-, svg- or png-files and tables as csv- or excel-files.


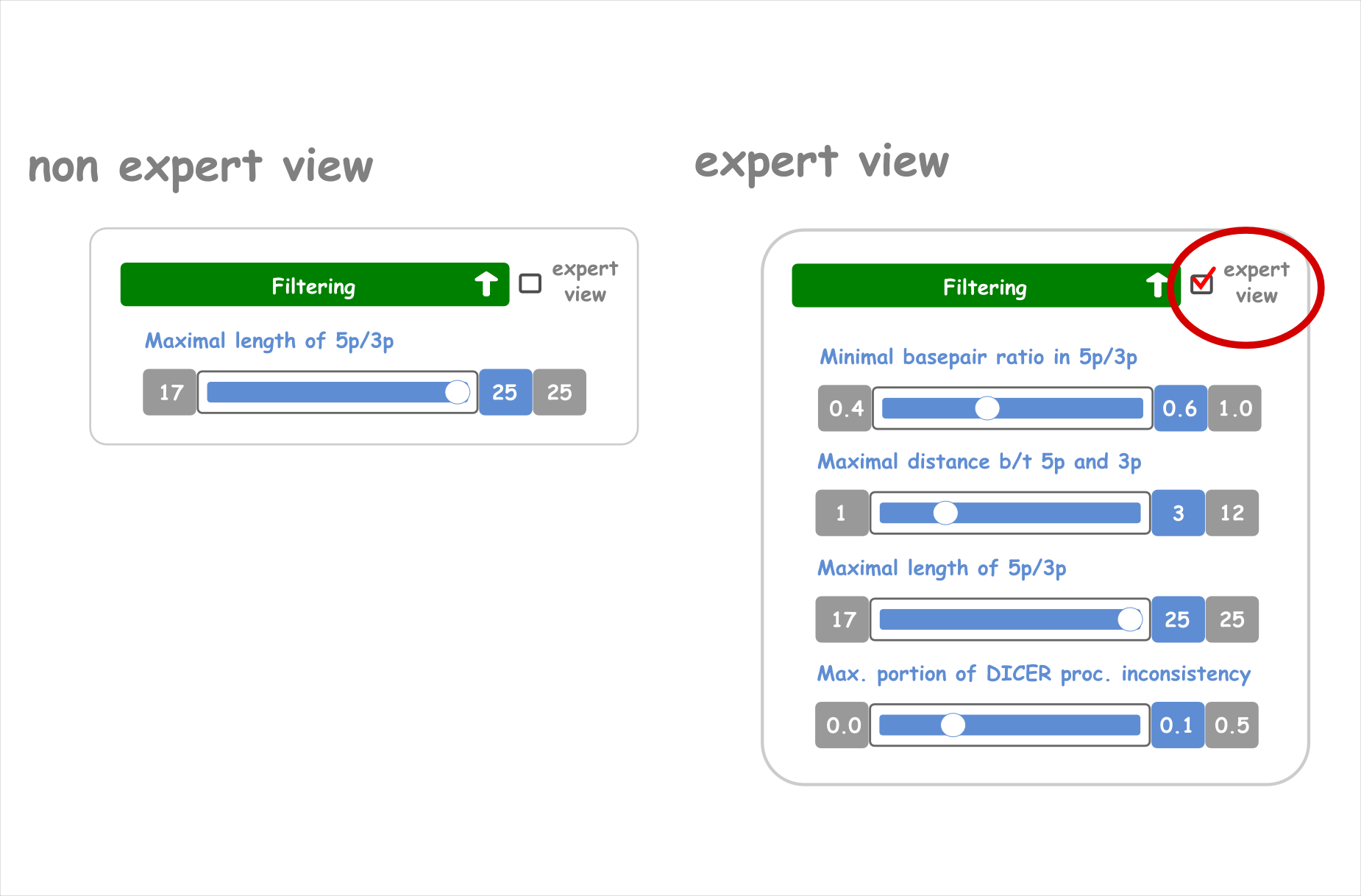
Clear Overview of the Parameters
For each analysis step, we provide a standard and an expert view to keep an overview of the parameters.


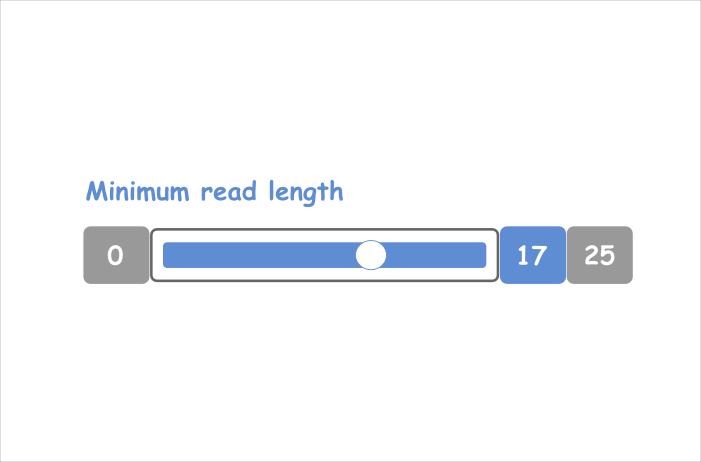
Range
We provide for each numerical parameter a range with minimum and maximum value to guide the user in a senseful way.


Help Message
If you hover with the cursor over the label of a parameter, a help message will pop up.
Additionally, some help messages contains an image to clear up misunderstandings.